
It’s important for practitioners who use the ControlLogix PAC to be aware of the different types of tasks and their use. Such a mismatch can result in significant difference in how the Integral and Derivative math is calculated.
Rslogix 500 pid update#
The timing associated with a continuous task usually varies between 15-30 milliseconds, while most PID controllers are set with a fixed update time of 500 milliseconds. If the scan rate for a controller’s task is set to “continuous,” then the task will execute the PID logic as quickly as possible and without regard for the actual sample rate of the PID. If a periodic task isn’t possible, a timer prior to the PID block can be used to fire the PID block at the correct interval. It’s considered best-practice to use periodic tasks rather than continuous tasks when tuning PIDs. Upon its completion the task will then permit the other lower priority tasks to resume where they left off. When the designated time arrives a periodic task will first interrupt all other tasks that have a lower priority and then perform its operation. The periodic task causes controller functions to be performed according to specified intervals. If an engineer needs to run a section of logic on a scheduled basis within the scan of other logic, then a periodic task is the way the controller should be configured. Periodic TasksĪs may be expected a periodic task runs intermittently. Only one continuous task can be run at a time. It’s worth noting that multiple continuous tasks cannot be run simultaneously on a controller.
Rslogix 500 pid full#
Once a full scan of the controller is completed the task will restart and run again immediately. That will cause the logic to run continuously in the background, and it will divert CPU power from other operations such as motion, communication, as well as periodic or event-specific tasks. If a technician needs a section of logic to run all the time, then the logic should be configured for operation as a continuous task. Like the name suggests a continuous task runs in an uninterrupted manner. Read on to learn more about these two types of tasks and what is considered best-practice for loop tuning.

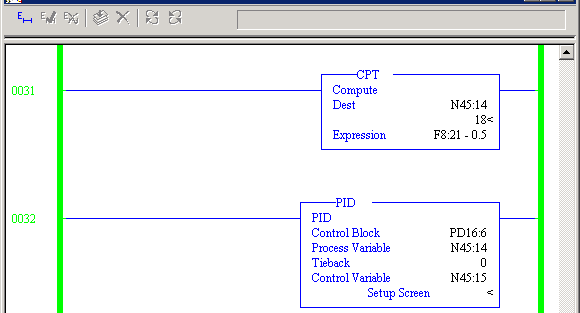
While the two modes are similar, there are important differences that directly affect how the PID functions and how it can be tuned for improved performance. It’s not uncommon for the PID block to be configured to run as a continuous task versus a periodic task. The root of the problem is frequently linked to the way in which the ControlLogix PAC’s ladder logic is executed.
Rslogix 500 pid software#
What’s more, since the issue stems from a data mismatch, commercial PID loop tuning software won’t be able to provide a better answer. If the PID block is executed significantly faster than its configured update time during a PID controller tuning session, it can be expected that the outcome will leave something to be desired from a controller performance standpoint. For instance, if the PID Block’s update time is set to 500 milliseconds, the rung on which the PID block is located also needs to execute at 500 milliseconds. More specifically, when the PID block is executed in the PAC it needs to match the update time configured in the PID block.
Have you ever seen an Integral Term on a PID controller that seems an order of magnitude larger or smaller than what should be used? Often, the issue stems from the method in which logic is executed on the Process Automation Controller (PAC).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
